Unleashing the Power of Convolutional Neural Networks: A Breakdown of their Advantages and Training Process
Introduction
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have revolutionized the field of computer vision, enabling remarkable achievements in image recognition and analysis. In this blog article, we will delve into the advantages of using CNNs and explore the process of training these networks with labeled data. Understanding these concepts will empower you to harness the potential of CNNs and apply them to various computer vision tasks.
Advantages of Convolutional Layers
To truly appreciate the power of CNNs, let’s consider an example. Imagine you have a 32 by 32 by 3 dimensional image, and you want to apply a 5 by 5 filter with six filters. Using fully connected layers in this scenario would require an enormous number of parameters—around 14 million. However, by using convolutional layers, each filter only requires 25 parameters plus a bias parameter, resulting in a total of just 156 parameters. The significant reduction in parameters is due to two key advantages of convolutional layers: parameter sharing and sparsity of connections.
Parameter sharing takes advantage of the fact that a feature detector, such as a vertical edge detector, useful in one part of an image is likely useful in another part. By applying the same feature detector across different positions in the image, CNNs reduce the number of parameters needed, making them more efficient to train. This concept holds true for both low-level features like edges and higher-level features like facial recognition.
The sparsity of connections further enhances the efficiency of CNNs. Each output unit in a convolutional layer depends only on a subset of input features, allowing for focused computation. Irrelevant input features have minimal impact on the output, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the network.
Training a Convolutional Neural Network
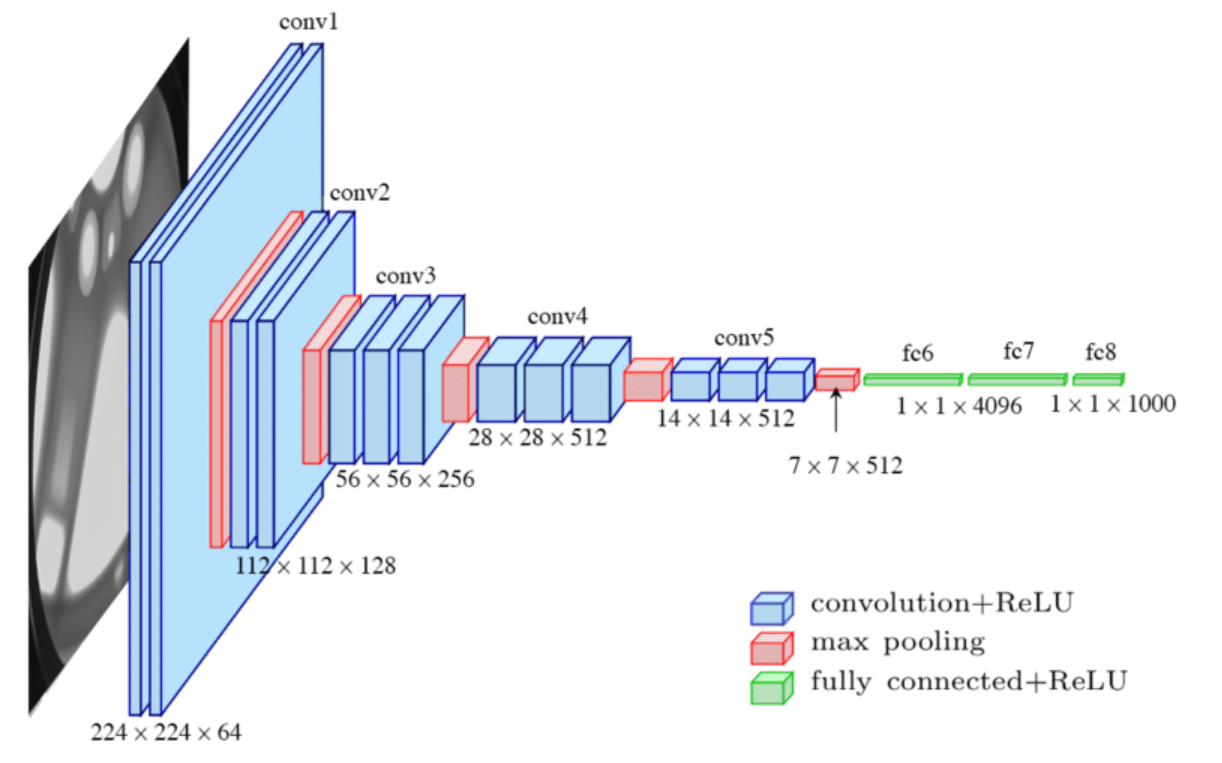
To train a CNN, we need a labeled training dataset. Consider building a cat detector using a CNN structure consisting of convolutional and pooling layers, followed by fully connected layers and a softmax output. The network’s parameters, weights (W) and biases (B), are initialized randomly.
The training process involves optimizing these parameters to minimize a cost function. By summing the losses of the network’s predictions on the entire training set and dividing by the number of examples, we obtain the cost function (J). Gradient descent or other optimization algorithms are then employed to iteratively update the parameters based on the gradients of the cost function. The goal is to find the optimal parameter values that result in accurate predictions.
CNNs excel at capturing translation invariance, meaning they can recognize objects even when they are shifted or transformed slightly. This property is achieved by applying the same filters across different positions in the image. The network learns to encode robust features and becomes more adept at handling variations in object positions.
Conclusion
Convolutional Neural Networks have emerged as a powerful tool in computer vision, offering superior performance in image recognition and analysis tasks. By leveraging the advantages of parameter sharing and sparsity of connections, CNNs significantly reduce the number of parameters, making them more manageable and less prone to overfitting.
Training a CNN involves optimizing the network’s parameters using labeled training data. Through iterative updates based on the gradients of the cost function, the CNN learns to make accurate predictions. This process, combined with the network’s ability to capture translation invariance, results in effective object detectors and classifiers.
In future articles, we will explore concrete examples of successful CNN architectures, enabling you to recognize effective network structures for different applications. Additionally, we will delve into various computer vision applications, such as object detection and neural style transfer, opening up a world of possibilities with CNNs.
Unleash the power of CNNs in your computer vision projects, and stay tuned for more insights
and practical tips in our upcoming articles.