Summary: Pooling Layers in Convolutional Neural Networks
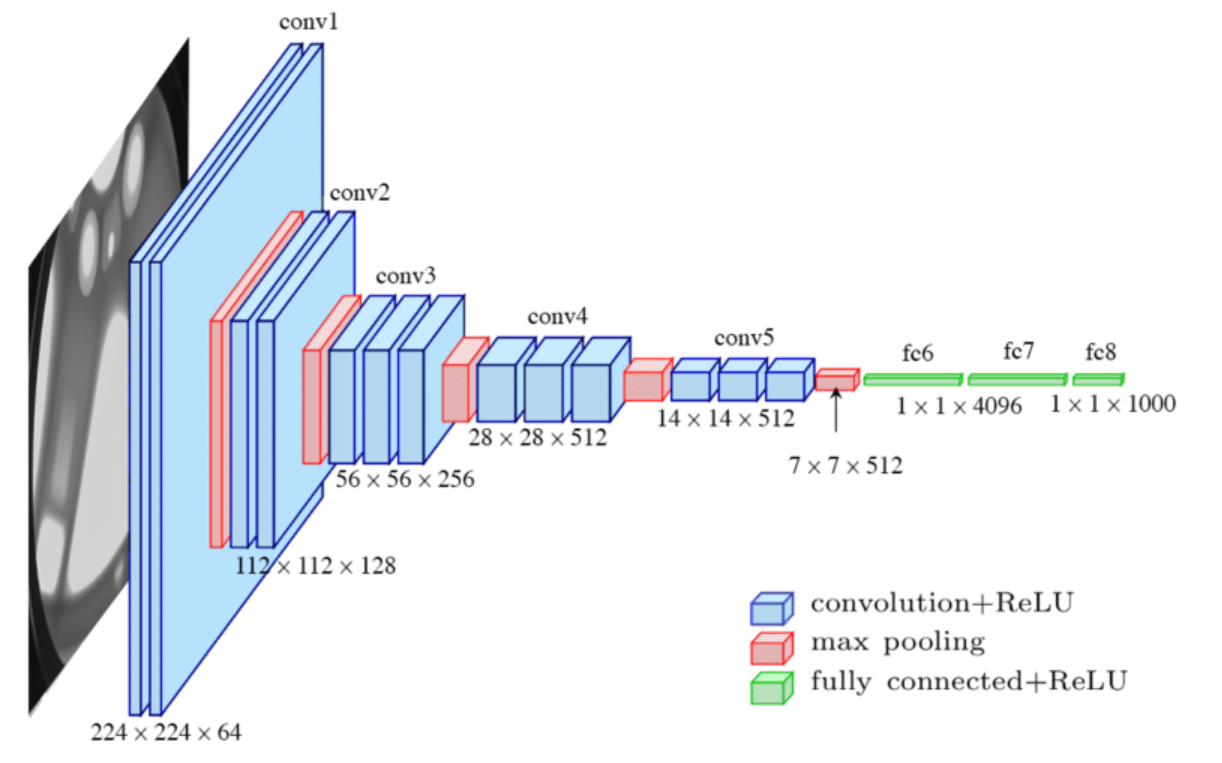
In Convolutional Neural Networks (ConvNets), pooling layers are often used alongside convolutional layers to reduce the size of the representation and enhance certain features’ robustness. This blog post summarizes the key concepts and operations involved in pooling layers.
Max Pooling
- Max pooling is a commonly used pooling technique in ConvNets.
- It aims to downsample the input representation while preserving the most prominent features.
- The process involves dividing the input into regions, typically squares, and taking the maximum value within each region.
- The size of the pooling filter (f) determines the region size, and the stride (s) specifies the step size for moving the filter across the input.
- The output of max pooling is a reduced representation, where each element corresponds to the maximum value within its corresponding region.
Intuition Behind Max Pooling
- Max pooling aims to preserve detected features within the input.
- If a particular feature exists anywhere within a region, the maximum value in that region remains high in the output.
- Features that are not detected consistently across the regions result in lower maximum values in the output.
- The underlying reason for the effectiveness of max pooling is not fully understood, but it has been found to work well in practice.
Hyperparameters of Max Pooling
- The hyperparameters of max pooling include the filter size (f) and the stride (s).
- Common choices for hyperparameters are f = 2 and s = 2, which reduce the height and width of the representation by a factor of 2.
- Padding (p) can be added to the input, but it is rarely used in max pooling.
Pooling in 3D Inputs
- When dealing with 3D inputs, such as multiple channels, max pooling is performed independently on each channel.
- The output dimensions remain the same as the input, but the pooling operation is applied to each channel separately.
Average Pooling
- Average pooling is another type of pooling, where the average value within each region is taken instead of the maximum.
- While max pooling is more commonly used, average pooling has limited applications, except for collapsing representations in very deep networks.
Learning and Parameters
- Pooling layers have no parameters to learn.
- The hyperparameters of the pooling layer, such as filter size and stride, are set manually or through cross-validation.
- Pooling is a fixed function applied during network computation.
Understanding pooling layers is essential for grasping the downsampling and feature preservation aspects of ConvNets. While max pooling is the preferred choice in many cases, average pooling can also be useful in specific scenarios. By setting the appropriate hyperparameters, pooling layers contribute to the overall efficiency and robustness of ConvNets.