EfficientNet: Scaling Neural Networks for Optimal Performance
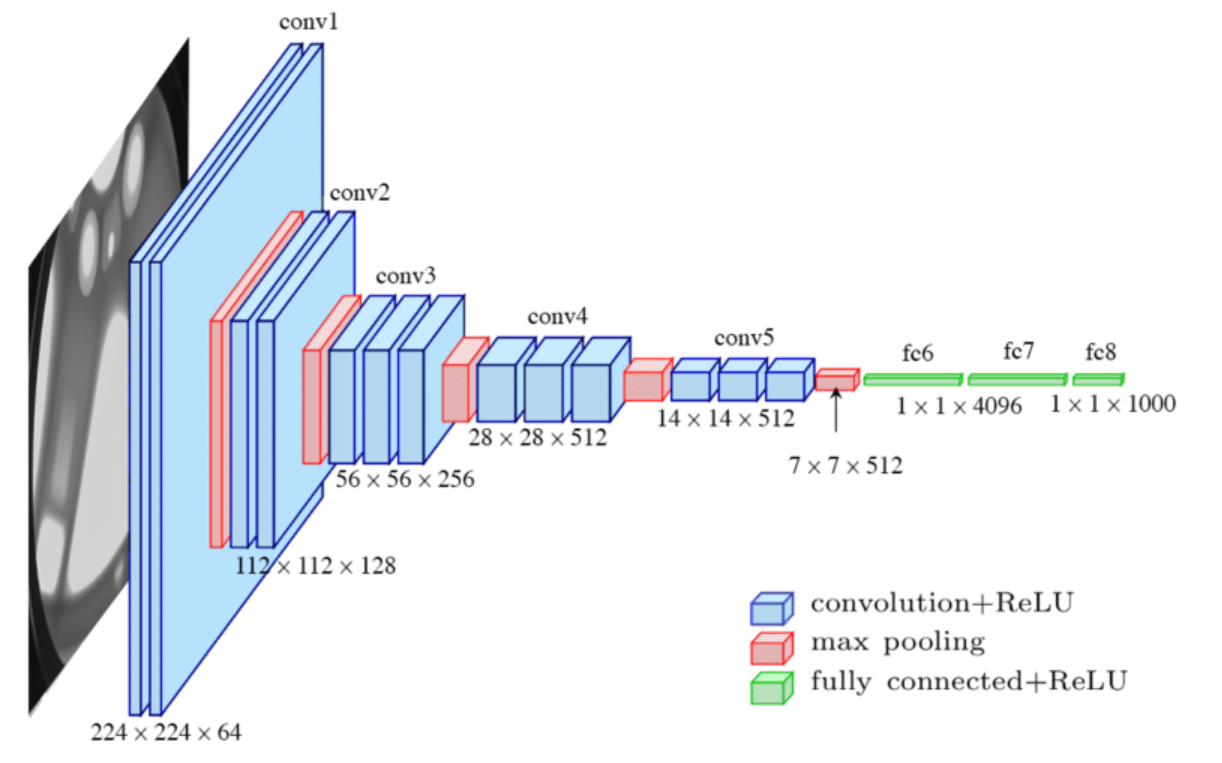
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, developing neural networks that can efficiently adapt to different devices and computational resources is crucial. This is where EfficientNet comes into play. EfficientNet is an architecture that enables the scaling of neural networks while optimizing their performance based on specific device requirements. In this blog post, we will explore the key concepts behind EfficientNet and how it empowers developers to create efficient and adaptable neural networks.
The Three Scaling Parameters: r, d, and w
EfficientNet introduces three essential parameters for scaling neural networks: image resolution (r), network depth (d), and layer width (w). These parameters allow developers to fine-tune their networks to match the available computational budget of the target device.
1. Image Resolution (r)
By adjusting the image resolution, developers can strike a balance between the level of detail required for accurate predictions and the computational resources available. Scaling up the resolution enhances the network’s ability to capture finer details, but it comes at the cost of increased computation. Conversely, scaling down the resolution reduces the computational burden, sacrificing some level of detail in the process.
2. Network Depth (d)
Network depth refers to the number of layers in the neural network. Increasing the depth allows for more complex representations to be learned, potentially improving the network’s performance. However, deeper networks require more computational resources. Adjusting the depth allows developers to find the optimal trade-off between performance and computational efficiency.
3. Layer Width (w)
Layer width relates to the number of channels in each layer of the network. Widening the layers can enhance the representation power of the network, potentially leading to improved accuracy. However, wider layers also increase computational demands. Developers can adjust the layer width to find the right balance between accuracy and efficiency.
Compound Scaling: Finding the Optimal Trade-Off
EfficientNet goes beyond individual parameter scaling by introducing compound scaling. This approach involves simultaneously adjusting the image resolution, network depth, and layer width to achieve the desired network configuration. By finding the optimal trade-off between these parameters, developers can create neural networks that deliver optimal performance within the given computational budget.
Leveraging Open-Source Implementations
Determining the ideal scaling rates for efficient network design can be challenging. However, the open-source community provides valuable resources and implementations of EfficientNet that can assist developers in selecting appropriate scaling ratios. These resources offer practical guidelines and insights to help developers make informed decisions based on their specific device constraints.
Embracing Efficiency and Adaptability
EfficientNet bridges the gap between computational efficiency and network adaptability. By combining the principles of EfficientNet with techniques like MobileNet, developers can create neural networks that are both computationally efficient and flexible enough to operate on a wide range of devices. This opens up possibilities for developing applications in domains where computational and memory limitations are significant concerns.
EfficientNet empowers developers to design neural networks that are tailored to the computational resources available on various devices. As technology continues to advance, incorporating efficiency and adaptability into network design becomes increasingly important. With EfficientNet, developers can achieve the optimal balance between performance and resource utilization, driving innovation and unlocking the full potential of neural networks.